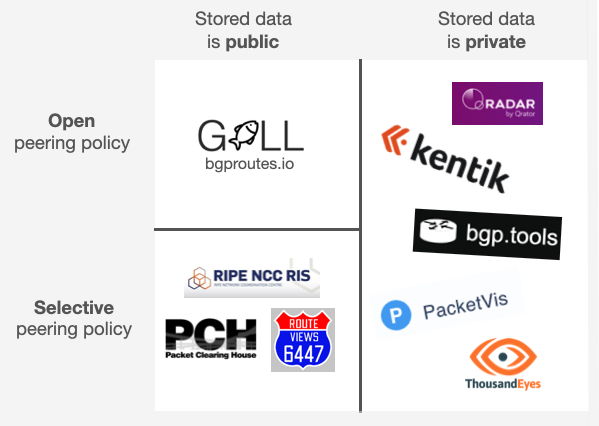
GILL offers a fundamentally different approach compared to existing BGP collection platforms.
It stands out by providing an open peering policy and making all collected data
publicly accessible to the entire community.
This is achievable because GILL selectively stores only the most valuable data,
thereby reducing costs.
In contrast, other platforms either keep their data confidential or implement selective peering policies.
An overview of the BGP route collection platforms landscape.
Why you should consider peering with GILL
✅ United we stand. By peering with GILL, you will share your RIB and every BGP route update that you observe with the entire community. In return, you can monitor how the BGP updates of your interest propagate across the Internet thanks to the other networks that peer with GILL.
✅ We need all of you. Whether you are a large Tier-1 AS, a small stub AS, or any other AS on the Internet, we welcome you to peer with GILL. Unlike other public BGP route collection platforms that selectively accept new peers, GILL takes a more inclusive approach and welcomes everyone.
✅ It is easy and fast. There is nothing easier than peering with GILL. Everything is automated. It should take less than ten minutes of your time and only requires a few lines of configuration on one of your BGP router.
✅ Clear data sharing policy. We believe in transparency regarding what happens with the data GILL collects. Our data sharing policy is straightforward, helping you make informed decisions about whether to peer with GILL. Our leitmotiv is that the data stored on our servers will always be publicly available.
What you should pay attention to with GILL
❗ Some data is discarded. To save resources, GILL selectively stores BGP route updates rather than retaining all collected data. The selection process employs peer-reviewed algorithms designed to eliminate redundant information, ensuring that only essential updates are preserved.
❗ Peering is only possible with BGP multihop. While this simplifies the architecture of GILL, it also means that your BGP session with GILL may pass through multiple ASes. We are actively working to enhance the security of these BGP multihop sessions to prevent vulnerabilities from third-party adversarial inputs. In any case, peering sessions with GILL are strictly for monitoring purposes and will not impact your other critical BGP sessions.
Start peering with GILL and contribute BGP data
❗ GILL is currently in prototype mode and operates on a small VM. In the short term, we may need to impose limitations on the number of peers and the volume of data we store. These limitations will be lifted once GILL transitions to production mode, and we are working hard to make that happen!
 LL
LL